Earlier today I got into a friendly discussion and debate on Twitter about a new web site called W3Fools. The site bills itself as a “W3Schools intervention”, and the purpose is to wake developers up to the fact that W3School tutorials can, and do, have errors.
The problem with a site like W3Fools, I said (using shorter words, or course, since this was Twitter), is that it focuses too much on the negative aspects of W3Schools, without providing a viable alternative.
But, they said, W3Fools does provide links to other sites that provide information on HTML, CSS, or JavaScript. And, I was also told, the reason W3Schools shows up first in search results is because of uncanny use of SEO optimization.
Hmmm.
It may be true that W3Schools makes excellent use of SEO, and it may be equally true that W3Schools commits egregious and painful errors. However, neither of these account for what W3Schools is doing right. If you don’t acknowledge what the site does well, you’re not going to make much headway into turning people off the site—no matter how many cleverly named sites you create.
For instance, one of the superior information sites recommended by W3Fools is the Mozilla Doc Center, or MDC as it is affectionately known. Now, I’m a big fan of MDC. I use it all the time, especially when I want to get a better idea of what Firefox supports. But look at the work you have to put in to learn about a new HTML5 element, such as the new HTML5 hgroup element:
- Go to main page
- Click on HTML5 link
- Search through the topics until you see one that’s titled “Sections and outlines in HTML5”, which you know you want because it mentions hgroup
- Have a neuron fire and realize that you can just click directly on hgroup
- Go to the hgroup page, past the disclaimer about what version of Firefox supports the element, looking for an example of usage
- Realize there is no example of how to use hgroup
- Go to the original Sections and Outlines in HTML5 link
- Go past some stuff about elephants, looking for example
- Go past some bullets about why all this new sectioning stuff is cool, looking for an example
- Break down and use your in-page search to find hgroup
- Finally find an example of how to use hgroup
As compared to W3Schools:
- Go to main page
- Click on Learn HTML5 link
- Click on New Elements link
- Start to scroll down when you realize the new elements are listed along the left side
- Click on hgroup
- Look at example
One thing W3Schools does well is provide a clean, simple to navigate interface that makes it very easy to find exactly what you need with a minimum of scrolling or searching.
Returning to our comparison between W3Schools and MDC, we then search for information on SQL. Oh, wait a sec: there isn’t anything on SQL at the Mozilla site. That’s because Mozilla is primarily a browser company and is only interested in documenting browser stuff.
So then our intrepid explorer must find another site, this one providing information on SQL. And if they want to learn more about PHP, they have to find yet another site. To learn about ASP? Another site, and so on.
What W3Schools also provides is one-stop shopping for the web developer. Once you’ve become familiar with the interface, and once the site has proved helpful, you’re more likely to return when you need additional information. Let’s face it: wouldn’t you rather use one site than dozens?
Let’s say, though, that you need information on CSS3. Well, you know that MDC covers CSS, so you return to the MDC site, and you click on the link that’s labeled “CSS”, and you look for something that says CSS3.
What do you mean there isn’t anything that says CSS3? What do you mean that transitions are CSS3—how am I, a CSS3 neophyte, supposed to know this?
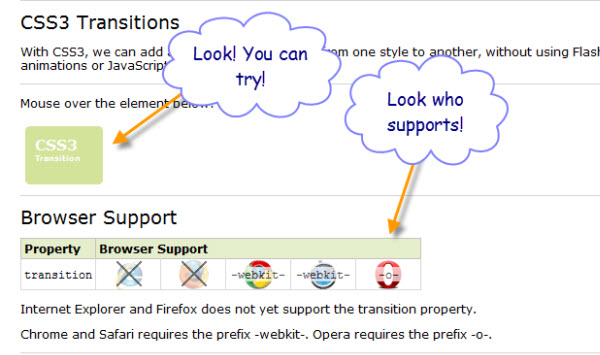
Returning to W3Schools, I click the link in the main page that is labeled CSS3. Oh look, in the page that opens, there’s a sidebar link that’s labeled “CSS3 transitions”. And when I click that link, a page opens that provides an immediate example of using CSS3 transitions that I can try, as well as an easy to read a table of browser support.
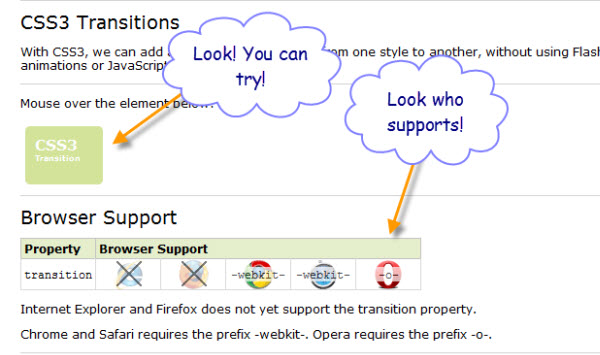
W3Schools doesn’t throw a lot of text before the examples, primarily because we learn web material best by example. Remember that an entire generation of web developers grew up with “View Source” as our primary learning tool.
But so far, I’ve only compared W3Schools to MDC. There are other useful sites that the W3Fools site approves. So I try the “Google: HTML, CSS, and JavaScript from the ground up” web page. When it opens, I click the link labeled CSS…
And I get a video about using CSS.
A video.
Remember in junior high or high school, when your science teacher would bring out the projector and you knew you were going to get a video? Do you remember that feeling that came over you? How you kind of relaxed, because you know the teacher wasn’t going to ask you any questions, and you didn’t have to write any notes, or even really pay attention?
I bet some of you even fell asleep during the video.
Videos are good for specific types of demonstrations—when something is complex, with many different steps, and the order of the steps and other factors have to be just so.
When it comes to CSS, HTML, and so many other web technologies, though, video is about the most passive and non-interactive learning experience there is. More importantly, if the video doesn’t have captioning, and most don’t, you’re also leaving part of your audience behind.
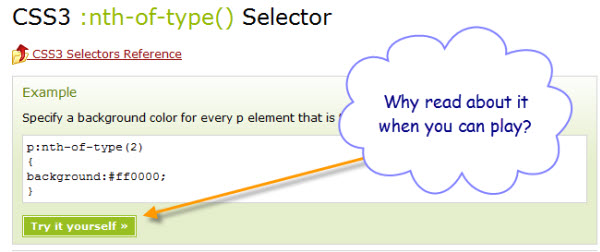
Now let’s return to the W3Schools site, this time looking at one of the CSS selector tutorials. The first thing you notice is that right below the example there’s a button, labeled “Try it Yourself”.
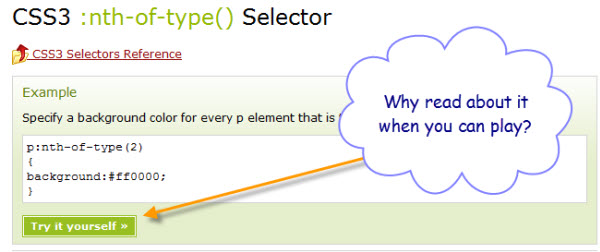
Why read about it, when you can play?
One of the more annoying aspects of trying to learn about a specific HTML element, or a bit of CSS, is that you have to create an entire web page just to try it out. What W3Schools provides is that all important, absolutely essential, one button click to Try it out.
I’m not defending W3Schools. The site has played off the W3C title, though that doesn’t have a lot of meaning nowadays. More importantly, some of the material has errors and the site is resistant to correcting any of these errors, and this is unconscionable.
But you aren’t going to dent the popularity of the site without at least understanding why it is so popular. The W3Schools’ site is not popular because of SEO, and it’s not popular because of the W3 part of the name.
The W3Schools website is so popular because it is so usable.